Cell adhesion: the first step of cancer metastasis and our anti-adhesion study
YuTing Fang
Cell adhesion, literally, means cell adhere to some certain surfaces. In vivo, it refers to the linkage or adhesion between cells. It also stands for a manner of communication among cells. The media for this communication is some soluble cytokines named cell-adhesion molecules(CAM). CAM contains multiple molecules inducing the cell-adhesion and cell-contact, staying a certain and unique molecular structure which helps them identify the specific receptors on the surface before the adhesion occurs.
CAM works in a ligand-receptor manner, involving cell identification, cell activation, signal transference, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and its movements. It is the molecular basement for a series of physiological process like immune response, inflammation, coagulation, cancer metastasis and wound healing.
CAM was once defined as the proteins contribute to extracellular matrix such as Laminin (LN), fibronectin (FN) and etc. It has been redefined as a molecule family recently. Given that the various receptors in ECM, CAM is, now, known as a big family including multifarious molecules. Due to the adherent efficiency for cellular adhesion in vitro, molecules belonged to CAM are called cell adhesion molecule. Still, the mechanisms of CAM in vivo need further exploration.
Adhesion manner among cells is one of the main studying projects about CAM. Homo-connection and hetero-connection separately refers to the adhesion between cells belong to the same type and different types. Calcium dependent adhenin and NCAM are two famous cell adhesion molecules in the homo-connection manner while most CAM induce hetero-connection between cells.
People also study on the physiological function of CAM. Cell adhesion is the reflection of cells nature to maintain their structure and function. CAM was referred as some transmembrane proteins such as thy-1 and LFA-3. Now, we considered CAM not only bridge cells, but also take charge of the information exchange of cells. For instance, concentrated tyrosine kinase is found in transmembrane proteins which implies CAM being capable of transferring signals.
There are several methods for naming the CAM.
1. Name after function, like ICAM,VCAM,TCR,LFA-1 and etc.
2. Named by CD.
The CAM named by CD are called by a joint name that is CD molecule.
Scope of the definition for CAM and CD.
*Pink stands for cytokines on the cell surface; blue stands for the CAM; yellow stands for CD molecule.
For the recent 5 years, people have identified CAM related to cell adhesion via clone techniques. The whole CAM family can be divided into 5 big families. With further development, more and more CAM are expected to be found and explained.
①integrin family
The basic structure for integrin family:
Heterodimer and transmembrane molecule consisting of α,βsubunit.
Distribution of Integrin family.
Integrin is wide spread. One kind of integrin is distributed on several kinds of cells in the mutual way. The level of integrin expression varies according to the cell differentiation and proliferation.
②selectin family
③Ig superfamily
④cadherin family
⑤mucin-like family
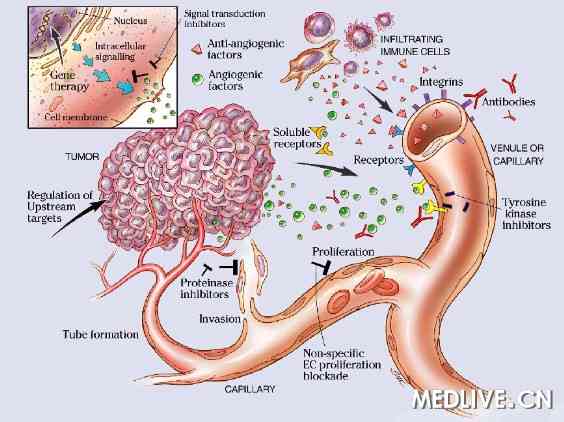
Integrin, existed on the surface of cells, induce the adhesion between cells and the adhesion between cells and ECM, having great impacts on the cell proliferation and cancer metastasis. Selectin mainly focus on mediating the hetero-adhesion between different cell types and the cellular movements. The level of selectin expression depends on the organs where metastasis happens. It contributes significantly to circulating tumor cells for recognizing vascular endothelial cells in targeting organs. Cadherins, a kind of transmembrane protein dependent on calcium, mediates the homo-adhesion. At present, cadherin intimately related to the cancer invasion and metastasis, especially for E-cadherin.
CAM works in a lot of ways.It can regulate the immune cells in a mutual way by recognizing the specific receptor. It is involved in the inflammation by induce the adhesion between leukocyte and vascular endothelial cells. It also helps lymphocyte homing and recycling.
In addition, cell adhesion is intimately involved in cancer metastasis. During the process of tumor cells invasion, cancer cells will forwardly invade the basal membrane which can be divided into 3 steps. The first step is the attachment of cancer cells. The second step is the degradation of the basal membrane and the third step is the migration through the basal membrane of cancer cells. The whole process contains homo-adhesion between cells and hetero-adhesion between cancer cells and basal membrane. Therefore, the cell adhesion plays a significant role in cancer metastasis. On one hand, with the loosening among cancer cells, cancer cells have a chance get separation with tumor, taking the first step on metastasis. On the other hand, cancer cells adhere to excellular matrix and vascular endothelial cells,then intravasate into vasculature and disseminate via blood circulation. To summarize, although we have come a long way on studying the process of cancer metastasis. The details and mechanisms still require further explanation so that we can apply them into novel therapies.
At present, many scientific research institutions have already studied on cell anti-adhesion. For instance, the function and deactivation of CAM was explored in the cases of immunological disease which can be used as efficient therapy on diverse illness even with the risk for interference on normal immunity.
Quantities of members in the CAM family have a soluble form which are able to generate spontaneously, existed in a high concentration in many inflammation and cancer-like diseases. In spite of the misty mechanism, it is pretty clear these soluble forms of CAM plays as competitive inhibitors to CAM which implies value to medical therapy.
In conclusion, we identified many specific CAMs and did quantities of research on them. Now we have found common characteristics between cell-cell adhesion and cell-matrix adhesion as well as ones between mechanisms of mechanical and chemical signaling. Thus, cellular anti-adhesion and its clinical application will be the novel global research focus in the next decades.
For now, our center is working on this project. Developing CMAPC-tu, CMAPC-mei, CMAPC-jiu as safe and efficient drugs for metastasis prevention. Hopefully they are capable of safely and effectively interfering cancer metastasis after surgery in a long term. Therefore, patients can be relieved from fear of potential cancer metastasis, and cancer death rate can be significantly reduced.

