1.The definition of cancer and its inducement
Tumor is coming from normal somatic cells. In which case, somatic cells goes wild due to a series of mutation on gene resulted from internal or external pathogenic inducements. These somatic cells grow in a uncontrolled manner and then gradually becomes a new tissue which can be called tumor. Tumors can be categorized as benign tumor and malignant tumor and all kinds of malignancy are named as cancer. There are generally two types of inducements caused cancer: carcinogenesis from gene and environment. The former one includes the activation of oncogene or the deactivation of anti-oncogene and the modulation of apoptotic genes. The latter one includes chemical carcinogenesis (PAH, nitrosamines, etc.), physical carcinogenesis (ionizing radiation), carcinogenesis resulted from virus and bacteria.
2. The differences between benign and malignant tumors
①Differentiation: Differentiation between benign tumors and normal tissues is not so obvious with low heteromorphism. While the differentiation of the malignant tumors is severe with high heteromorphism compared to normal tissue.
②Mitosis: Mitosis stays common in malignant tumors with some pathological ones while it stays none or seldom in benign tumors.
③Speed of growth: Malignant tumors grow fast while benign tumors grow slowly.
④Manner of growth: Benign tumors grow in exophytic and expansile manner. The latter one usually happens with envelope as a clear boundary among the normal tissues which means the tumors can be pushed. On the contrary, malignant ones grow in a invasive manner with no clear boundaries.
⑤Secondary lesion: Malignant tumors usually happen with necrosis and hemorrhage or even ulceration which cannot be observed commonly in benign tumors.
⑥Metastasis: Metastasis usually happens after the excision of malignant tumors.
⑦Relapse: Relapse often happens in the patients having malignant tumor instead of Benign tumors.
⑧Influence on organs: The impacts from benign tumors usually limit to stress or obstruction and the ones from malignant tumors go way beyond obstruction. Malignant tumors can also cause damage to the primary and secondary site of normal tissues during the metastasis, resulting in the necrosis, hemorrhage and infection.
3. Will tumors disappear on their own?
There is no definite boundaries between benign and malignant tumors. And the malignancy among malignant tumors are various according to the specific type. Some of the benign tumors are able to transfer in to a malignant one. Furthermore, it is pretty rare that one or two kinds of malignant tumor might stop growing and even fade away on its own.
4. Is tumor inheritable?
Some autosomal dominant inheritable tumors do not present as a malignant disease. But they have malignant potentiality. It usually attacks on the early age of people, coming with cancer metastasis on the bilateral organs. In terms of autosomal recessive inheritable tumors, people who suffered from them takes a great risk having some genetic defects. Inducements from gene and environment have synergistic effects on tumor attacks and the environmental factors contribute more. The tumor inheritability involves multi gene segments. For now, we have found that various types of tumors have family history such as breast cancer, intestinal cancer, esophagus cancer, liver cancer, nasopharynx cancer and etc.
5. Advantages and disadvantages of therapies on caner nowadays.
①Surgery: Once the tumor was determined, it should be excised as soon as possible. Surgery on the early stage of cancer can acquire a successful rate over 90 percent. But when tumors comes to the third stage, patients will take a great risk of relapse and metastasis after surgery.
②radiotherapy: Radiotherapy requires sensibility of tumors cells to the radiation. It also requires the avoidance of normal tissues from the radiation. However, from time to time, radiotherapy may cause some side effects like radiodermatitis, radiation esophagitis, nausea and etc.
③Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy are known as using drugs which can destroy both tumor cells and somatic cells to treat cancer. It has extremely low successful rate on cancer metastasis with high toxicity.
④Photodynamic therapy: Photodynamic therapy using certain wavelength of light to activate certain chemicals called photosensitizer. And when photosensitizer comes back to steady state from excited state, it will release singlet oxygen to kill partial tumor cells. This kind of therapy requires patients to stay in the dark for a few days to excrete the photosensitizer.
⑤Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy takes out the immune cells of patients and treat them with certain conditions so that these cells are able to identify the tumor cells. Then, these immune cells are transported back into the patients, resulting in the activation of specific immunity response and degrading the tumors in some patients. The immunotherapy avoid the damage to somatic cells and normal functions of human body. Without series of side effects like what chemotherapy and radiotherapy has, immunotherapy suits cancer patients for all the stages and all the habitus.
⑥symptomatic supportive treatment: This kind of treatment is intended for reliving the pain and improving the quality of life for patients. The treatment itself cannot heal the tumor, but it can prevent the deterioration of health.
Although the anti-cancer drug has already shown some acquirement, this kind of drug still cannot reduce the death rate by cancer. The main reasons might be the ones below: ①the anti-cancer drug cannot save patients’ lives when metastasis has already happened.
②the toxicity of anti-cancer drugs makes them restricted on low dose.
③Targeting drug works only on few people.
④The mutation of targeting protein caused endogenous or exogenous drug tolerance to the anti-cancer drugs.
⑤Anti-cancer drugs are not intended for the prevention of metastasis with extremely low efficiency on quiescent tumor cells.
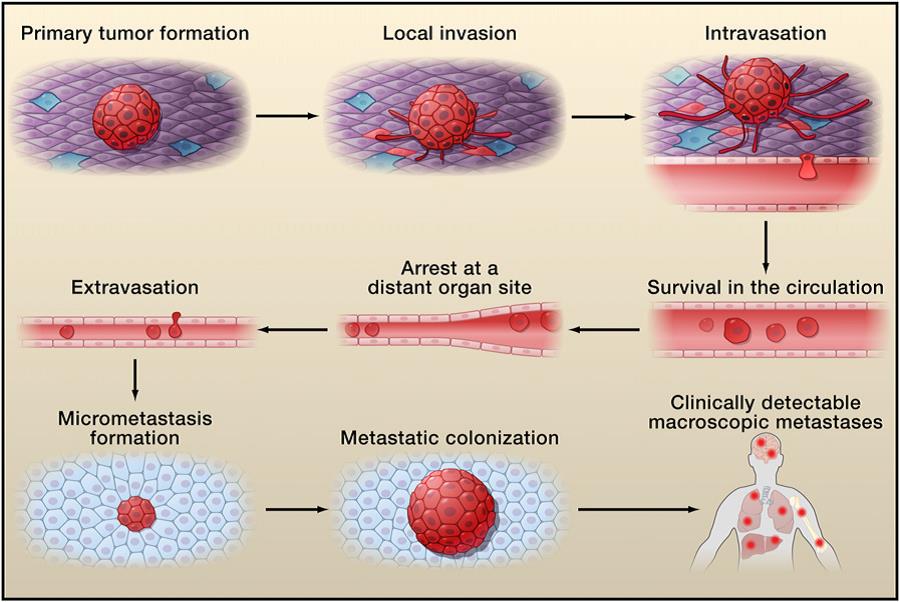
6. Manners and Mechanisms of Cancer Metastasis
Malignant tumor grows in an invasive manner. Malignant tumor cells are able to not only proliferate in the primary site, but also diffuse to other parts of human body by
several approaches including the ones below:
①Direct extension: tumor cells grows through the gap among the tissues, damaging to the adjacent normal organs for further proliferation. This phenomenon can be observed usually in the terminal cancer.
②Metastasis: with the intravasation and the extravasation, tumor cells get to reach targeting organs via vasculature and continues to grow into a metastasis nodules similar as the tumor in the primary site.
This kind of dissemination is only found in malignant tumors which can be divided into several general approaches via lymph circulation, blood circulation and implantation metastasis.
The metastasis nodules present preference on certain organs. Such as the colon cancer metastasis happens mostly on liver and the pulmonary cancer metastasis happens on adrenal gland and brain. The mechanisms behind these phenomena are still under exposure. It is supposed that the tumor cells needs specific ligand to connect with adhesion molecule on the surface of them which happens to exist on the endothelial cells of the vessels in certain organs, or that these certain organs are able to release the chemicals attractive to tumor cells. This kind of preference of metastasis on certain organs provide us an entrance to develop approaches for the prevention of cancer metastasis.
7.Prevention for Cancer Metastasis
For the last half century, death rate of other severe diseases(heart attack) has been reduced drastically (over 60 percent) while the death rate of cancer has been reduced only around 5 percent. Among the cases of cancer, most patients die of cancer metastasis. Which is why cancer metastasis becomes a global, urgent and significant problem.
The Cancer Metastasis Prevention Drug (CMPD)should focus on:
①The chemicals must stay in low toxicity when CMPD is intended for people without clinical symptoms.
②Patients should start taking in CMPD as soon as being diagnosed as cancer and could not break dosing at least for 5 years.
③Chemical interference is synthetical, containing multiple efficient monomers worked on different cellular pathways of cancer metastasis.
Therefore, to reach our goal, we must study the mechanisms of metastasis from cellular and molecular basis as well as from mammal body as a whole discovering key pathways that control cancer metastasis; establishing animal models that can reliably mimic metastasis in patients. After comprehensive understanding of metastasis dynamics, internal and external elements that deactivate or reactivate circulating tumor cells, we will develop various methods, techniques and products that can be reliably alert metastasis for cancer survivors; develop various techniques and products (including drug combination, nanomaterials , biopharmaceuticals, traditional Chinese medicines, acupunctures and others) that can efficiently and safely prevent cancer survivors from potential metastasis. Therefore, patients can be relieved from fear of potential cancer metastasis, and cancer death rate can be significantly reduced.
Dr Jia, Chairman of Drug Development Institution in AAPS(2008-2012), taken in The Recruitment Program of Global Experts in China. Mainly working on the anti-cancer drugs, Cardiovascular drugs, NO drugs and nanopharmaceuticals. Establishing the Cancer Metastasis Alert and Prevention Centre in 2012.

